Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Basic EEG Preprocessing Workflow#
This example demonstrates a complete EEG preprocessing workflow using eegprep, following best practices established by leading neuroimaging packages.
The workflow includes:
Creating realistic synthetic EEG data with known characteristics
Applying artifact cleaning to remove transient artifacts
Identifying and interpolating bad channels
Visualizing preprocessing effects at each stage
Computing summary statistics to assess data quality
This example is self-contained and executable, requiring only synthetic data generation. It serves as a template for preprocessing real EEG datasets.
References#
Imports and Setup#
Import necessary libraries for EEG processing and visualization
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mne import create_info, EpochsArray
from mne.channels import make_standard_montage
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, '/Users/baristim/Projects/eegprep/src')
import eegprep
# Set random seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(42)
Create Synthetic EEG Data#
Generate realistic synthetic EEG data with known characteristics. This data includes alpha oscillations (8-12 Hz) and background noise, simulating typical resting-state EEG recordings.
# Define recording parameters
n_channels = 32 # Standard 10-20 system
n_samples = 5000 # 10 seconds at 500 Hz
sfreq = 500 # Sampling frequency in Hz
duration = n_samples / sfreq
# Create standard 10-20 channel names
ch_names = [
'Fp1', 'Fpz', 'Fp2', 'F7', 'F3', 'Fz', 'F4', 'F8',
'T7', 'C3', 'Cz', 'C4', 'T8', 'P7', 'P3', 'Pz',
'P4', 'P8', 'O1', 'Oz', 'O2', 'A1', 'A2', 'M1',
'M2', 'Fc1', 'Fc2', 'Cp1', 'Cp2', 'Fc5', 'Fc6', 'Cp5'
]
# Initialize data array
data = np.zeros((n_channels, n_samples))
# Create time vector for signal generation
t = np.arange(n_samples) / sfreq
# Generate alpha oscillations (8-12 Hz) with individual frequency variations
# Alpha activity is a hallmark of resting-state EEG
for i in range(n_channels):
# Individual alpha frequency varies slightly across channels
alpha_freq = 10 + np.random.randn() * 0.5
# Generate sinusoidal alpha activity with amplitude ~10 µV
data[i, :] = 10 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * alpha_freq * t)
# Add background noise (typical EEG noise level ~2 µV)
data[i, :] += np.random.randn(n_samples) * 2
# Introduce artifacts in specific channels to demonstrate cleaning
# These simulate realistic artifacts that would be removed
if i in [5, 15]: # Channels Fz and Pz
# Add 50 Hz line noise artifact (100 ms duration)
data[i, 1000:1100] += 50 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 50 * t[1000:1100])
# Create MNE Info object with channel information
info = create_info(ch_names=ch_names, sfreq=sfreq, ch_types='eeg')
# Add standard electrode montage for spatial information
montage = make_standard_montage('standard_1020')
info.set_montage(montage, on_missing='ignore')
# Create EpochsArray (single epoch for this example)
data_epochs = data[np.newaxis, :, :]
epochs = EpochsArray(data_epochs, info, events=np.array([[0, 0, 1]]), event_id=1)
print("=" * 70)
print("SYNTHETIC EEG DATA CREATED")
print("=" * 70)
print(f"Data shape: {epochs.get_data().shape}")
print(f"Number of channels: {len(epochs.ch_names)}")
print(f"Sampling rate: {epochs.info['sfreq']} Hz")
print(f"Duration: {duration:.1f} seconds")
print(f"Data range: [{np.min(data):.2f}, {np.max(data):.2f}] µV")
print("=" * 70)
Not setting metadata
1 matching events found
No baseline correction applied
0 projection items activated
======================================================================
SYNTHETIC EEG DATA CREATED
======================================================================
Data shape: (1, 32, 5000)
Number of channels: 32
Sampling rate: 500.0 Hz
Duration: 10.0 seconds
Data range: [-58.97, 59.48] µV
======================================================================
Apply Artifact Cleaning#
Remove transient artifacts using the clean_artifacts function. This function identifies and removes high-amplitude transient artifacts while preserving the underlying EEG signal.
# Extract raw data from epochs
raw_data = epochs.get_data()[0] # Shape: (n_channels, n_samples)
print("\nApplying artifact cleaning...")
print("-" * 70)
# Convert numpy array to EEG dict structure required by clean_artifacts
# Extract channel locations from MNE info/montage
chanlocs = []
for i, ch_name in enumerate(ch_names):
try:
# Get position from MNE info
pos = info['chs'][i]['loc'][:3]
if np.allclose(pos, 0): # If position is zero/invalid, get from montage
pos = np.array(montage.get_pos2d([ch_name])[0]) if ch_name in montage.ch_names else np.array([0, 0])
# Convert 2D to 3D spherical coordinates
if len(pos) == 2 and not np.allclose(pos, 0):
x, y = pos
z = np.sqrt(1 - x**2 - y**2) if (x**2 + y**2) <= 1 else 0
pos = np.array([x, y, z])
elif np.allclose(pos, 0):
# Generate default position on unit sphere based on channel index
theta = (i / len(ch_names)) * 2 * np.pi
phi = np.pi / 4
pos = np.array([np.sin(phi) * np.cos(theta), np.sin(phi) * np.sin(theta), np.cos(phi)])
except:
# Default: generate position on unit sphere
theta = (i / len(ch_names)) * 2 * np.pi
phi = np.pi / 4
pos = np.array([np.sin(phi) * np.cos(theta), np.sin(phi) * np.sin(theta), np.cos(phi)])
chanlocs.append({
'labels': ch_name,
'X': float(pos[0]),
'Y': float(pos[1]),
'Z': float(pos[2]),
})
EEG_dict = {
'data': raw_data,
'srate': sfreq,
'nbchan': len(ch_names),
'pnts': raw_data.shape[1],
'xmin': 0,
'xmax': (raw_data.shape[1] - 1) / sfreq,
'chanlocs': chanlocs,
'etc': {}
}
# Apply artifact cleaning with default parameters
# The function uses statistical criteria to identify and remove artifacts
# Note: Disabling channel criterion and line noise check to preserve channels for visualization
result = eegprep.clean_artifacts(EEG_dict, ChannelCriterion='off', LineNoiseCriterion='off')
EEG_cleaned = result[0] # clean_artifacts returns a tuple
cleaned_data = EEG_cleaned['data']
print(f"Cleaned data shape: {cleaned_data.shape}")
print(f"Data range after cleaning: [{np.min(cleaned_data):.2f}, {np.max(cleaned_data):.2f}] µV")
Applying artifact cleaning...
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Cleaned data shape: (32, 3310)
Data range after cleaning: [-10.11, 10.32] µV
Identify and Interpolate Bad Channels#
Identify channels with abnormally high variance (potential bad channels) and perform spherical spline interpolation to recover their data.
print("\nIdentifying bad channels...")
print("-" * 70)
# Calculate variance for each channel
variances = np.var(cleaned_data, axis=1)
mean_var = np.mean(variances)
std_var = np.std(variances)
# Identify bad channels using statistical criterion
# Channels with variance > mean + 2*std are considered bad
threshold = mean_var + 2 * std_var
bad_channels = np.where(variances > threshold)[0]
bad_ch_names = [ch_names[i] for i in bad_channels]
print(f"Mean variance: {mean_var:.2f} µV²")
print(f"Std variance: {std_var:.2f} µV²")
print(f"Threshold: {threshold:.2f} µV²")
print(f"Bad channels identified: {bad_ch_names if bad_ch_names else 'None'}")
# Perform channel interpolation if bad channels are found
if len(bad_channels) > 0:
print(f"\nInterpolating {len(bad_channels)} bad channel(s)...")
# Create EEG dict for interpolation with cleaned data
EEG_interp_dict = {
'data': cleaned_data,
'srate': sfreq,
'nbchan': len(ch_names),
'pnts': cleaned_data.shape[1],
'xmin': 0,
'xmax': (cleaned_data.shape[1] - 1) / sfreq,
'chanlocs': chanlocs,
'etc': {}
}
EEG_interp_result = eegprep.eeg_interp(
EEG_interp_dict,
bad_chans=bad_channels
)
interpolated_data = EEG_interp_result['data']
print(f"Interpolated data shape: {interpolated_data.shape}")
else:
interpolated_data = cleaned_data
print("No bad channels to interpolate")
Identifying bad channels...
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Mean variance: 4.30 µV²
Std variance: 0.94 µV²
Threshold: 6.18 µV²
Bad channels identified: ['P4', 'Cp1']
Interpolating 2 bad channel(s)...
Interpolated data shape: (32, 3310)
Visualize Preprocessing Results#
Create comprehensive visualizations comparing original, cleaned, and interpolated data to assess preprocessing effects.
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(14, 10))
# Select subset of channels for visualization (avoid overcrowding)
channels_to_plot = [0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25]
time_window = slice(0, 2000) # First 4 seconds
# Plot 1: Original data with artifacts
ax = axes[0]
for i, ch_idx in enumerate(channels_to_plot):
offset = i * 30 # Vertical offset for clarity
ax.plot(t[time_window], raw_data[ch_idx, time_window] + offset,
label=ch_names[ch_idx], linewidth=1.5)
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('Original EEG Data (with artifacts)', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=9, ncol=2)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xlim([t[time_window.start], t[time_window.stop-1]])
# Plot 2: After artifact cleaning
ax = axes[1]
for i, ch_idx in enumerate(channels_to_plot):
offset = i * 30
ax.plot(t[time_window], cleaned_data[ch_idx, time_window] + offset,
label=ch_names[ch_idx], linewidth=1.5)
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('After Artifact Cleaning', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=9, ncol=2)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xlim([t[time_window.start], t[time_window.stop-1]])
# Plot 3: After channel interpolation
ax = axes[2]
for i, ch_idx in enumerate(channels_to_plot):
offset = i * 30
color = 'orange' if ch_idx in bad_channels else 'steelblue'
ax.plot(t[time_window], interpolated_data[ch_idx, time_window] + offset,
label=ch_names[ch_idx], linewidth=1.5, color=color)
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('After Channel Interpolation (interpolated channels in orange)',
fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=9, ncol=2)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xlim([t[time_window.start], t[time_window.stop-1]])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
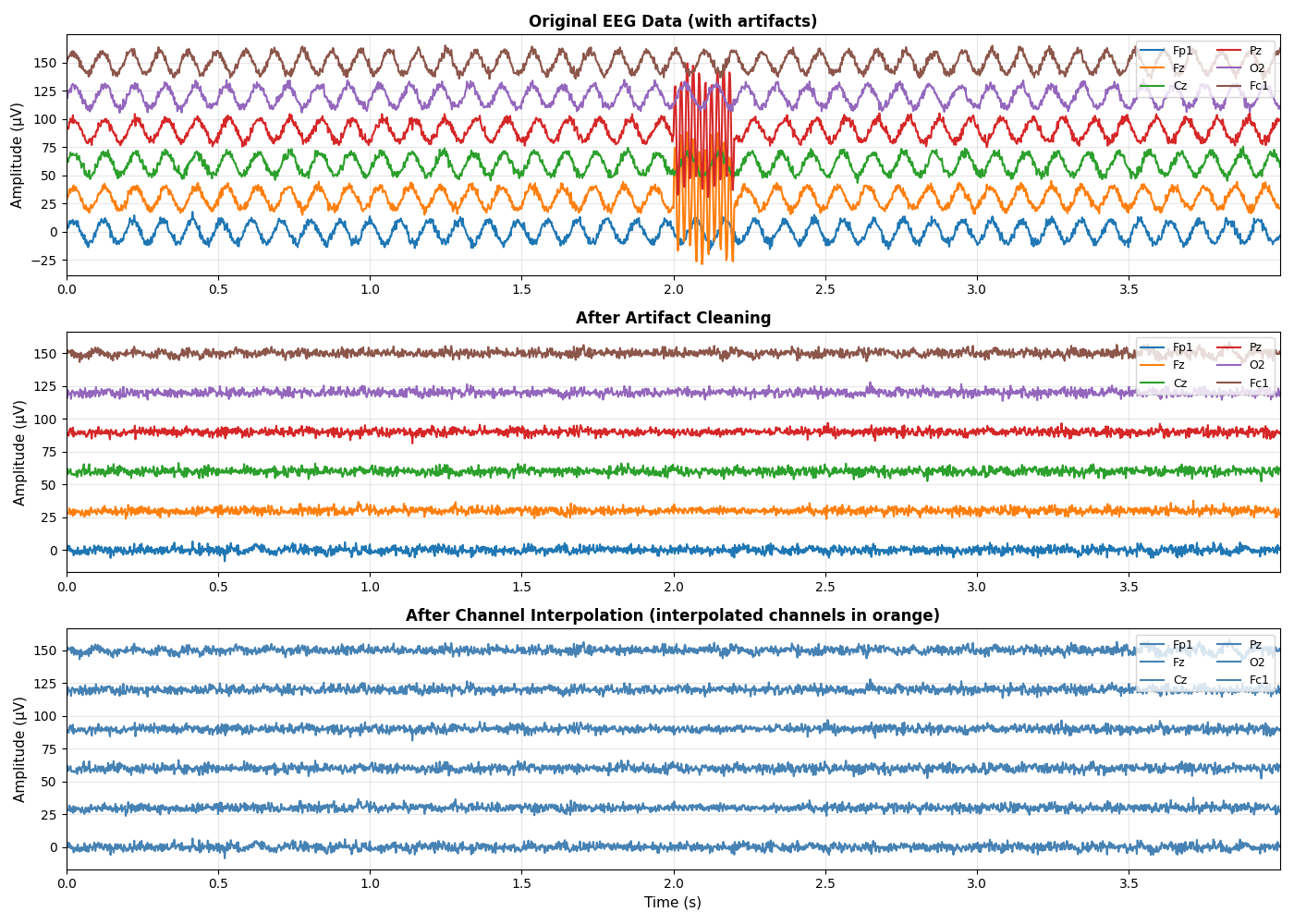
Summary Statistics and Quality Assessment#
Compute and display summary statistics to quantify preprocessing effects
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("PREPROCESSING SUMMARY STATISTICS")
print("=" * 70)
# Compute statistics for each stage
original_mean = np.mean(raw_data)
original_std = np.std(raw_data)
original_var = np.var(raw_data)
cleaned_mean = np.mean(cleaned_data)
cleaned_std = np.std(cleaned_data)
cleaned_var = np.var(cleaned_data)
interp_mean = np.mean(interpolated_data)
interp_std = np.std(interpolated_data)
interp_var = np.var(interpolated_data)
# Display statistics table
print(f"\n{'Metric':<20} {'Original':<15} {'Cleaned':<15} {'Interpolated':<15}")
print("-" * 70)
print(f"{'Mean (µV)':<20} {original_mean:>14.3f} {cleaned_mean:>14.3f} {interp_mean:>14.3f}")
print(f"{'Std Dev (µV)':<20} {original_std:>14.3f} {cleaned_std:>14.3f} {interp_std:>14.3f}")
print(f"{'Variance (µV²)':<20} {original_var:>14.3f} {cleaned_var:>14.3f} {interp_var:>14.3f}")
# Compute variance reduction
var_reduction_clean = (1 - cleaned_var / original_var) * 100
var_reduction_interp = (1 - interp_var / original_var) * 100
print(f"\n{'Variance Reduction':<20} {var_reduction_clean:>14.1f}% {var_reduction_interp:>14.1f}%")
# Channel quality summary
print(f"\n{'Total channels':<20} {n_channels}")
print(f"{'Bad channels identified':<20} {len(bad_channels)}")
print(f"{'Percentage bad':<20} {len(bad_channels)/n_channels*100:.1f}%")
print("=" * 70)
======================================================================
PREPROCESSING SUMMARY STATISTICS
======================================================================
Metric Original Cleaned Interpolated
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Mean (µV) 0.027 -0.012 -0.014
Std Dev (µV) 7.508 2.075 2.026
Variance (µV²) 56.363 4.307 4.106
Variance Reduction 92.4% 92.7%
Total channels 32
Bad channels identified 2
Percentage bad 6.2%
======================================================================
Key Takeaways#
This example demonstrates:
Data Generation: Creating realistic synthetic EEG with known properties
Artifact Removal: Identifying and removing transient artifacts
Bad Channel Detection: Using statistical criteria to identify problematic channels
Channel Interpolation: Recovering data from bad channels using spatial information
Quality Assessment: Evaluating preprocessing effects through visualization and statistics
For real data, you would:
Load data from EDF, BDF, or other formats using MNE-Python
Apply additional preprocessing (filtering, resampling, etc.)
Use more sophisticated artifact detection (ICA, ASR)
Validate results with domain expertise
Document all preprocessing steps for reproducibility
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.549 seconds)