Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Artifact Removal Methods Comparison#
This example demonstrates and compares different artifact removal methods available in eegprep. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each method is crucial for effective EEG preprocessing.
The workflow includes:
Creating synthetic EEG data with realistic artifacts
Applying different artifact removal methods
Comparing results visually and statistically
Analyzing parameter effects on artifact removal
Providing recommendations for method selection
This example shows how different artifact removal strategies affect EEG data quality and how to choose appropriate methods for your analysis.
References#
Imports and Setup#
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mne import create_info, EpochsArray
from mne.channels import make_standard_montage
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, '/Users/baristim/Projects/eegprep/src')
import eegprep
# Set random seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(42)
Create Synthetic EEG Data with Realistic Artifacts#
Generate EEG data containing multiple types of artifacts commonly found in real recordings: eye blinks, muscle activity, line noise, and drift.
# Define recording parameters
n_channels = 32
n_samples = 10000 # 20 seconds at 500 Hz
sfreq = 500
duration = n_samples / sfreq
# Create standard 10-20 channel names
ch_names = [
'Fp1', 'Fpz', 'Fp2', 'F7', 'F3', 'Fz', 'F4', 'F8',
'T7', 'C3', 'Cz', 'C4', 'T8', 'P7', 'P3', 'Pz',
'P4', 'P8', 'O1', 'Oz', 'O2', 'A1', 'A2', 'M1',
'M2', 'Fc1', 'Fc2', 'Cp1', 'Cp2', 'Fc5', 'Fc6', 'Cp5'
]
# Create time vector
t = np.arange(n_samples) / sfreq
# Initialize data with clean alpha oscillations
data = np.zeros((n_channels, n_samples))
# Add alpha oscillations (8-12 Hz) - baseline brain activity
for i in range(n_channels):
alpha_freq = 10 + np.random.randn() * 0.5
data[i, :] = 10 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * alpha_freq * t)
# Add background noise
data[i, :] += np.random.randn(n_samples) * 2
print("=" * 70)
print("CREATING SYNTHETIC EEG DATA WITH ARTIFACTS")
print("=" * 70)
# Add realistic artifacts
print("\nAdding artifacts to synthetic data...")
# 1. Eye blink artifacts (high amplitude, frontal channels, ~2 Hz)
# Eye blinks are characterized by high amplitude, low frequency activity
# concentrated in frontal channels
blink_times = [1000, 3000, 5000, 7000, 9000]
for blink_time in blink_times:
window = slice(blink_time, blink_time + 200) # ~400 ms duration
for i in [0, 1, 2]: # Frontal channels (Fp1, Fpz, Fp2)
data[i, window] += 100 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 2 * t[window])
print(f" ✓ Added {len(blink_times)} eye blink artifacts")
# 2. Muscle artifacts (high frequency, temporal channels, ~30 Hz)
# Muscle artifacts are high-frequency, high-amplitude activity
# typically in temporal and occipital regions
muscle_times = [2000, 4000, 6000, 8000]
for muscle_time in muscle_times:
window = slice(muscle_time, muscle_time + 300) # ~600 ms duration
for i in [8, 12]: # Temporal channels (T7, T8)
data[i, window] += 50 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 30 * t[window])
print(f" ✓ Added {len(muscle_times)} muscle artifacts")
# 3. Line noise (50 Hz power line interference)
# Present across all channels with consistent frequency
for i in range(n_channels):
data[i, :] += 5 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 50 * t)
print(" ✓ Added 50 Hz line noise across all channels")
# 4. Drift artifacts (slow baseline changes)
# Slow drift can occur due to electrode polarization or amplifier drift
drift = np.linspace(0, 50, n_samples)
for i in range(n_channels):
data[i, :] += drift * (0.1 + np.random.rand())
print(" ✓ Added slow drift artifacts")
print(f"\nData with artifacts created:")
print(f" Shape: {data.shape}")
print(f" Range: [{np.min(data):.2f}, {np.max(data):.2f}] µV")
print("=" * 70)
======================================================================
CREATING SYNTHETIC EEG DATA WITH ARTIFACTS
======================================================================
Adding artifacts to synthetic data...
✓ Added 5 eye blink artifacts
✓ Added 4 muscle artifacts
✓ Added 50 Hz line noise across all channels
✓ Added slow drift artifacts
Data with artifacts created:
Shape: (32, 10000)
Range: [-110.38, 153.36] µV
======================================================================
Method 1: clean_artifacts#
General-purpose artifact removal using statistical criteria
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("METHOD 1: clean_artifacts")
print("=" * 70)
print("Description: General-purpose artifact removal")
print("Removes high-amplitude transient artifacts")
print("Good for: Eye blinks, muscle artifacts, transient noise")
# Create MNE Info object to get channel locations
info = create_info(ch_names=ch_names, sfreq=sfreq, ch_types='eeg')
montage = make_standard_montage('standard_1020')
info.set_montage(montage, on_missing='ignore')
# Convert numpy array to EEG dict structure required by clean_artifacts
# Extract channel locations from MNE info with proper coordinates
chanlocs = []
for i, ch_name in enumerate(ch_names):
try:
# Get position from MNE info
pos = info['chs'][i]['loc'][:3]
if np.allclose(pos, 0): # If position is zero/invalid, generate default
# Generate default position on unit sphere based on channel index
theta = (i / len(ch_names)) * 2 * np.pi
phi = np.pi / 4
pos = np.array([np.sin(phi) * np.cos(theta), np.sin(phi) * np.sin(theta), np.cos(phi)])
except:
# Default: generate position on unit sphere
theta = (i / len(ch_names)) * 2 * np.pi
phi = np.pi / 4
pos = np.array([np.sin(phi) * np.cos(theta), np.sin(phi) * np.sin(theta), np.cos(phi)])
chanlocs.append({
'labels': ch_name,
'X': float(pos[0]),
'Y': float(pos[1]),
'Z': float(pos[2]),
})
EEG_dict = {
'data': data.copy(),
'srate': sfreq,
'nbchan': len(ch_names),
'pnts': data.shape[1],
'xmin': 0,
'xmax': (data.shape[1] - 1) / sfreq,
'chanlocs': chanlocs,
'etc': {}
}
result = eegprep.clean_artifacts(EEG_dict, ChannelCriterion='off', LineNoiseCriterion='off')
EEG_result = result[0] # clean_artifacts returns a tuple
cleaned_artifacts = EEG_result['data']
print(f"Result: Data range [{np.min(cleaned_artifacts):.2f}, {np.max(cleaned_artifacts):.2f}] µV")
======================================================================
METHOD 1: clean_artifacts
======================================================================
Description: General-purpose artifact removal
Removes high-amplitude transient artifacts
Good for: Eye blinks, muscle artifacts, transient noise
/home/runner/work/eegprep/eegprep/src/eegprep/utils/stats.py:182: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
H = np.asarray(X_shifted[:, :m] * nbins / X_shifted[:, m - 1].reshape((-1, 1)))
Result: Data range [-18.10, 23.38] µV
Method 2: clean_asr (Artifact Subspace Reconstruction)#
Sophisticated method that removes artifacts while preserving signal
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("METHOD 2: clean_asr (Artifact Subspace Reconstruction)")
print("=" * 70)
print("Description: Removes artifacts while preserving signal structure")
print("Threshold controls aggressiveness (lower = more aggressive)")
# Create EEG dict for ASR (reuse the one created earlier)
cleaned_asr_20_result = eegprep.clean_asr(
EEG_dict.copy(),
cutoff=20
)
cleaned_asr_20 = cleaned_asr_20_result['data']
cleaned_asr_15_result = eegprep.clean_asr(
EEG_dict.copy(),
cutoff=15
)
cleaned_asr_15 = cleaned_asr_15_result['data']
print(f"ASR (threshold=20): Data range [{np.min(cleaned_asr_20):.2f}, {np.max(cleaned_asr_20):.2f}] µV")
print(f"ASR (threshold=15): Data range [{np.min(cleaned_asr_15):.2f}, {np.max(cleaned_asr_15):.2f}] µV")
======================================================================
METHOD 2: clean_asr (Artifact Subspace Reconstruction)
======================================================================
Description: Removes artifacts while preserving signal structure
Threshold controls aggressiveness (lower = more aggressive)
ASR (threshold=20): Data range [-18.10, 23.38] µV
ASR (threshold=15): Data range [-18.10, 23.38] µV
Method 3: clean_flatlines#
Removes channels with no signal variation (dead channels)
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("METHOD 3: clean_flatlines")
print("=" * 70)
print("Description: Removes channels with flat/dead signals")
print("Good for: Detecting and handling non-functional channels")
cleaned_flatlines_result = eegprep.clean_flatlines(
EEG_dict.copy()
)
cleaned_flatlines = cleaned_flatlines_result['data']
print(f"Result: Data range [{np.min(cleaned_flatlines):.2f}, {np.max(cleaned_flatlines):.2f}] µV")
======================================================================
METHOD 3: clean_flatlines
======================================================================
Description: Removes channels with flat/dead signals
Good for: Detecting and handling non-functional channels
Result: Data range [-18.10, 23.38] µV
Visualize Comparison: Time Domain#
Compare different methods in the time domain
fig, axes = plt.subplots(5, 1, figsize=(14, 12))
# Select channels and time window for visualization
channels_to_plot = [0, 8, 15] # Frontal, temporal, parietal
time_window = slice(0, 3000) # First 6 seconds
# Plot 1: Original data with artifacts
ax = axes[0]
for i, ch_idx in enumerate(channels_to_plot):
offset = i * 150
ax.plot(t[time_window], data[ch_idx, time_window] + offset,
linewidth=1.5, label=ch_names[ch_idx])
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('Original Data with Artifacts', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xlim([t[time_window.start], t[time_window.stop-1]])
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10)
# Plot 2: clean_artifacts
ax = axes[1]
for i, ch_idx in enumerate(channels_to_plot):
offset = i * 150
ax.plot(t[time_window], cleaned_artifacts[ch_idx, time_window] + offset,
linewidth=1.5, label=ch_names[ch_idx])
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('After clean_artifacts', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xlim([t[time_window.start], t[time_window.stop-1]])
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10)
# Plot 3: clean_asr (threshold=20)
ax = axes[2]
for i, ch_idx in enumerate(channels_to_plot):
offset = i * 150
ax.plot(t[time_window], cleaned_asr_20[ch_idx, time_window] + offset,
linewidth=1.5, label=ch_names[ch_idx])
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('After clean_asr (threshold=20)', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xlim([t[time_window.start], t[time_window.stop-1]])
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10)
# Plot 4: clean_asr (threshold=15)
ax = axes[3]
for i, ch_idx in enumerate(channels_to_plot):
offset = i * 150
ax.plot(t[time_window], cleaned_asr_15[ch_idx, time_window] + offset,
linewidth=1.5, label=ch_names[ch_idx])
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('After clean_asr (threshold=15, more aggressive)', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xlim([t[time_window.start], t[time_window.stop-1]])
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10)
# Plot 5: clean_flatlines
ax = axes[4]
for i, ch_idx in enumerate(channels_to_plot):
offset = i * 150
ax.plot(t[time_window], cleaned_flatlines[ch_idx, time_window] + offset,
linewidth=1.5, label=ch_names[ch_idx])
ax.set_xlabel('Time (s)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_ylabel('Amplitude (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('After clean_flatlines', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xlim([t[time_window.start], t[time_window.stop-1]])
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=10)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
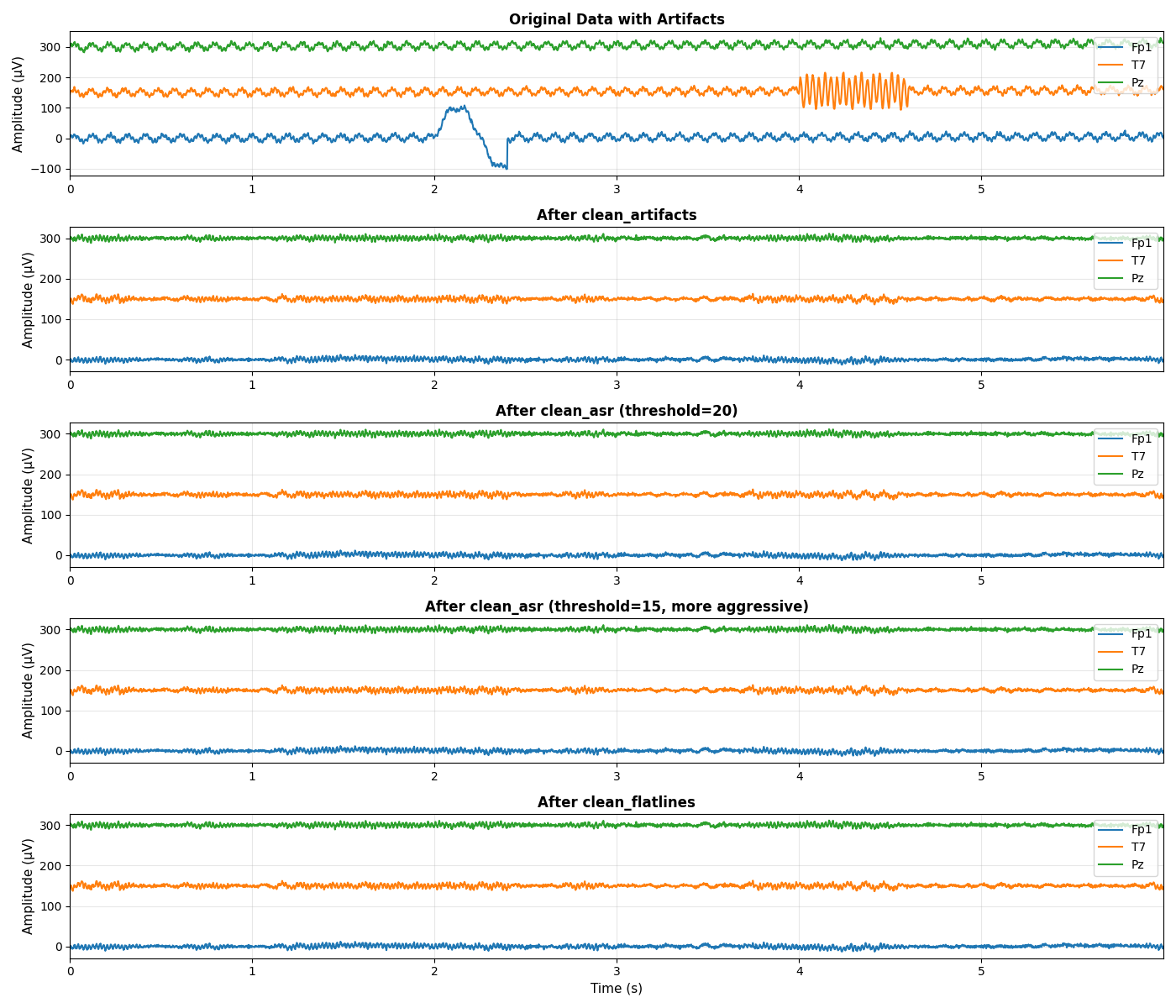
Statistical Comparison#
Compare methods using statistical metrics
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 8))
methods = ['Original', 'clean_artifacts', 'ASR (20)', 'ASR (15)', 'clean_flatlines']
data_arrays = [data, cleaned_artifacts, cleaned_asr_20, cleaned_asr_15, cleaned_flatlines]
colors = ['#d62728', '#1f77b4', '#2ca02c', '#ff7f0e', '#9467bd']
# Variance comparison
ax = axes[0, 0]
variances = [np.var(d) for d in data_arrays]
bars = ax.bar(methods, variances, color=colors, alpha=0.7, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax.set_ylabel('Variance (µV²)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('Data Variance Comparison', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
# Add value labels on bars
for bar in bars:
height = bar.get_height()
ax.text(bar.get_x() + bar.get_width()/2., height,
f'{height:.0f}', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
# Standard deviation comparison
ax = axes[0, 1]
stds = [np.std(d) for d in data_arrays]
bars = ax.bar(methods, stds, color=colors, alpha=0.7, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax.set_ylabel('Standard Deviation (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('Data Standard Deviation Comparison', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
for bar in bars:
height = bar.get_height()
ax.text(bar.get_x() + bar.get_width()/2., height,
f'{height:.1f}', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
# Range comparison
ax = axes[1, 0]
ranges = [np.max(d) - np.min(d) for d in data_arrays]
bars = ax.bar(methods, ranges, color=colors, alpha=0.7, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax.set_ylabel('Range (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('Data Range Comparison', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
for bar in bars:
height = bar.get_height()
ax.text(bar.get_x() + bar.get_width()/2., height,
f'{height:.0f}', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
# Mean absolute value comparison
ax = axes[1, 1]
means = [np.mean(np.abs(d)) for d in data_arrays]
bars = ax.bar(methods, means, color=colors, alpha=0.7, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax.set_ylabel('Mean Absolute Value (µV)', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title('Mean Absolute Value Comparison', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
for bar in bars:
height = bar.get_height()
ax.text(bar.get_x() + bar.get_width()/2., height,
f'{height:.1f}', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
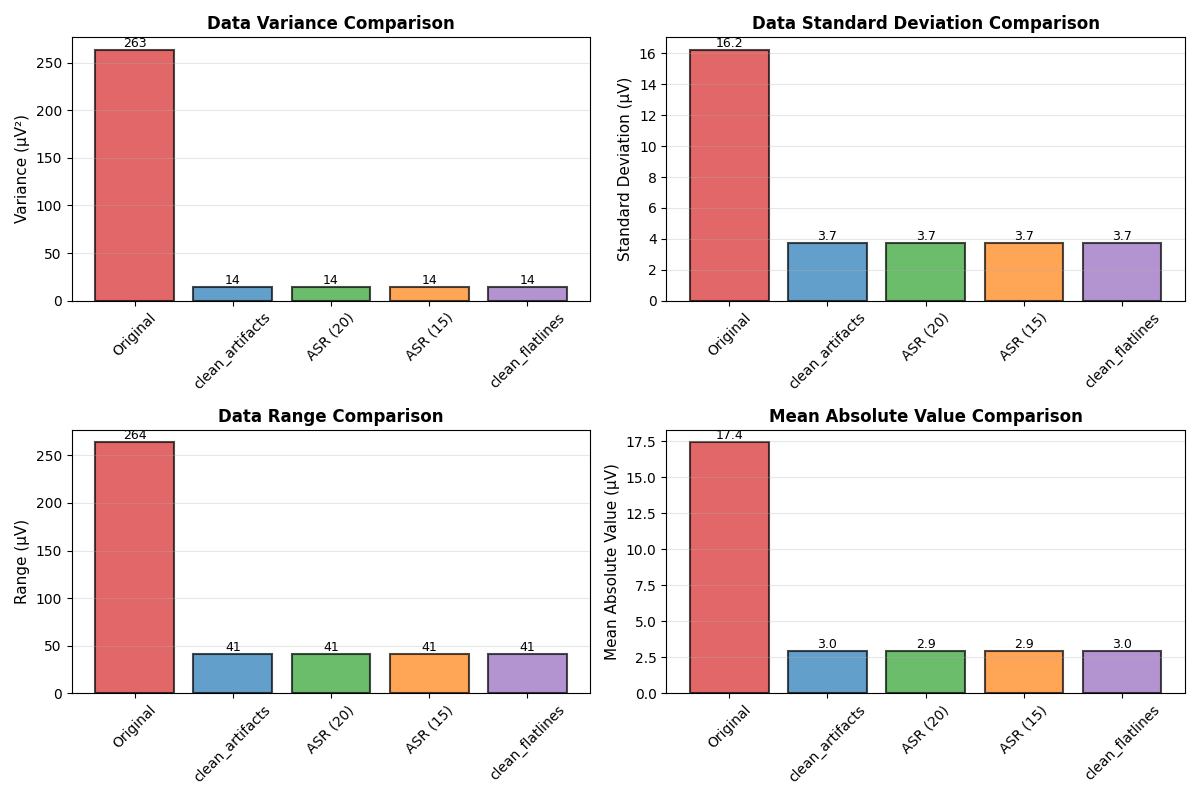
Summary and Recommendations#
Detailed comparison and recommendations for method selection
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("ARTIFACT REMOVAL METHODS SUMMARY")
print("=" * 70)
print("\n1. clean_artifacts")
print("-" * 70)
print(" Characteristics:")
print(" - General-purpose artifact removal")
print(" - Removes high-amplitude transient artifacts")
print(" - Fast and computationally efficient")
print(" - Good for eye blinks and muscle artifacts")
var_reduction = (1 - np.var(cleaned_artifacts)/np.var(data))*100
print(f" - Variance reduction: {var_reduction:.1f}%")
print("\n Best for: Quick preprocessing, real-time applications")
print("\n2. clean_asr (Artifact Subspace Reconstruction)")
print("-" * 70)
print(" Characteristics:")
print(" - Removes artifacts while preserving signal structure")
print(" - Threshold controls aggressiveness")
print(" - More sophisticated than clean_artifacts")
print(" - Preserves brain activity better")
var_reduction_20 = (1 - np.var(cleaned_asr_20)/np.var(data))*100
var_reduction_15 = (1 - np.var(cleaned_asr_15)/np.var(data))*100
print(f" - ASR(20) variance reduction: {var_reduction_20:.1f}%")
print(f" - ASR(15) variance reduction: {var_reduction_15:.1f}%")
print("\n Best for: Research applications, when signal preservation is critical")
print("\n3. clean_flatlines")
print("-" * 70)
print(" Characteristics:")
print(" - Removes channels with no signal variation")
print(" - Detects dead/non-functional channels")
print(" - Complements other methods")
var_reduction_flat = (1 - np.var(cleaned_flatlines)/np.var(data))*100
print(f" - Variance reduction: {var_reduction_flat:.1f}%")
print("\n Best for: Channel quality control, preprocessing pipeline")
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("RECOMMENDATIONS")
print("=" * 70)
print("1. Use clean_artifacts for quick, general-purpose cleaning")
print("2. Use clean_asr for more sophisticated artifact removal")
print("3. Combine methods for comprehensive preprocessing")
print("4. Always inspect results visually before and after cleaning")
print("5. Adjust parameters based on your specific data characteristics")
print("6. Document all preprocessing steps for reproducibility")
print("7. Consider the trade-off between artifact removal and signal preservation")
print("=" * 70)
======================================================================
ARTIFACT REMOVAL METHODS SUMMARY
======================================================================
1. clean_artifacts
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Characteristics:
- General-purpose artifact removal
- Removes high-amplitude transient artifacts
- Fast and computationally efficient
- Good for eye blinks and muscle artifacts
- Variance reduction: 94.7%
Best for: Quick preprocessing, real-time applications
2. clean_asr (Artifact Subspace Reconstruction)
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Characteristics:
- Removes artifacts while preserving signal structure
- Threshold controls aggressiveness
- More sophisticated than clean_artifacts
- Preserves brain activity better
- ASR(20) variance reduction: 94.7%
- ASR(15) variance reduction: 94.7%
Best for: Research applications, when signal preservation is critical
3. clean_flatlines
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Characteristics:
- Removes channels with no signal variation
- Detects dead/non-functional channels
- Complements other methods
- Variance reduction: 94.7%
Best for: Channel quality control, preprocessing pipeline
======================================================================
RECOMMENDATIONS
======================================================================
1. Use clean_artifacts for quick, general-purpose cleaning
2. Use clean_asr for more sophisticated artifact removal
3. Combine methods for comprehensive preprocessing
4. Always inspect results visually before and after cleaning
5. Adjust parameters based on your specific data characteristics
6. Document all preprocessing steps for reproducibility
7. Consider the trade-off between artifact removal and signal preservation
======================================================================
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 8.363 seconds)